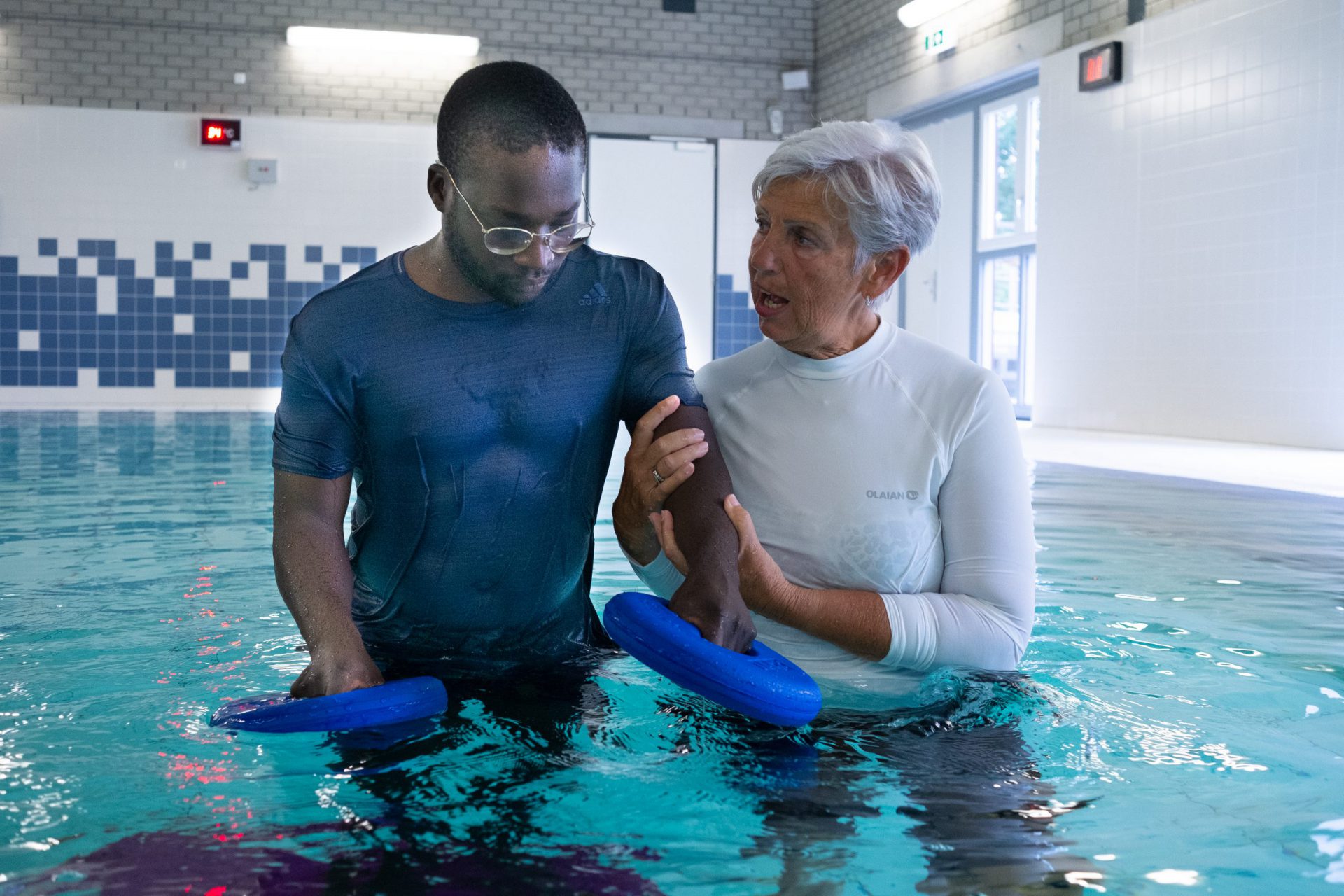
In aquatic therapy, several beneficial physical effects contribute to its efficacy. These include:
-1: Reduced weight bearing: The buoyancy of the water reduces the weight bearing on joints, which can help to reduce pain and inflammation.

-2: Increased range of motion: The resistance of the water can help to improve flexibility and range of motion, making it easier to perform exercises and movements.
-3: Improved cardiovascular fitness: Aquatic exercise can help to improve cardiovascular fitness, as the water provides resistance that can make the heart and lungs work harder.
-4: Increased muscle strength and endurance: Aquatic exercise can also help to improve muscle strength and endurance, as the water provides resistance that can make the muscles work harder.
-5: Improved balance and coordination: The water’s resistance can also help to improve balance and coordination by providing a challenging environment for movement.
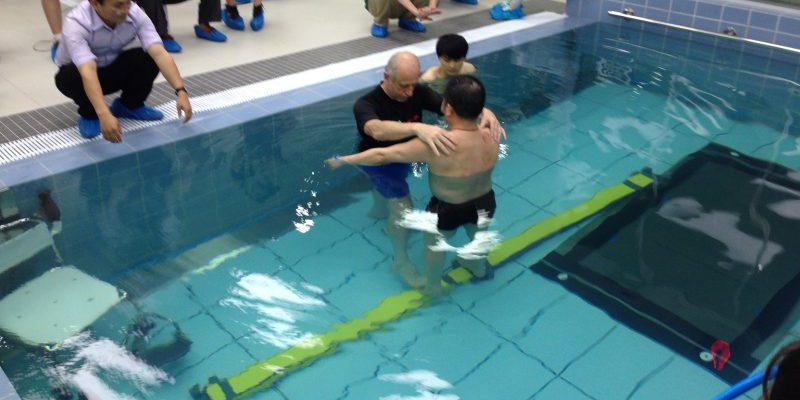

-6: Reduced stress on the body: The warm water and the buoyancy can reduce stress on the body, which can help to reduce pain and inflammation.
-7: Improved circulation: The warm water can help to improve circulation by dilating blood vessels and increasing blood flow to the muscles and joints.
-8: Increased proprioception: The water provides a challenging environment for movement which can help to improve proprioception, the ability to sense the position and movement of the body in space.



